professional factory for Mono-Crystalline 100W Solar Panel to Nepal Factory
Short Description:
We emphasize development and introduce new products into the market every year for professional factory for Mono-Crystalline 100W Solar Panel to Nepal Factory, We warmly welcome your participation based on mutual benefits in the near future.
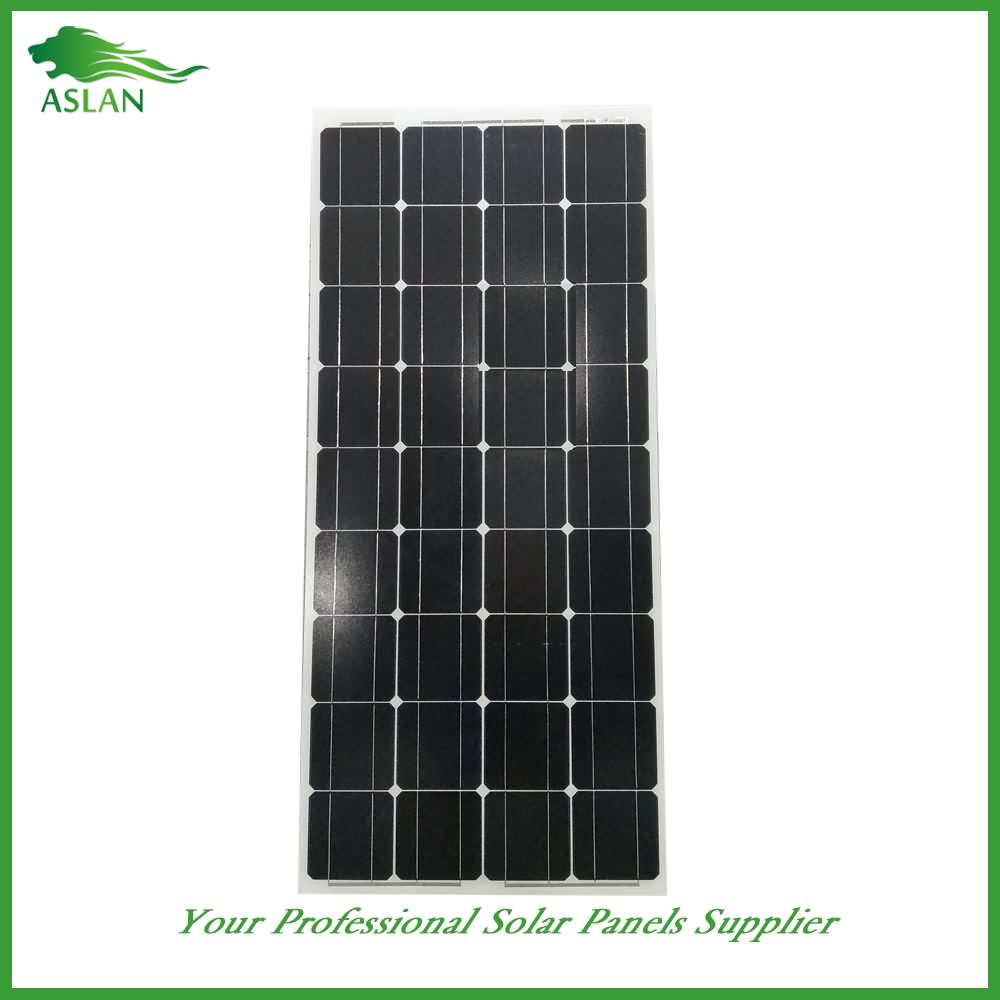
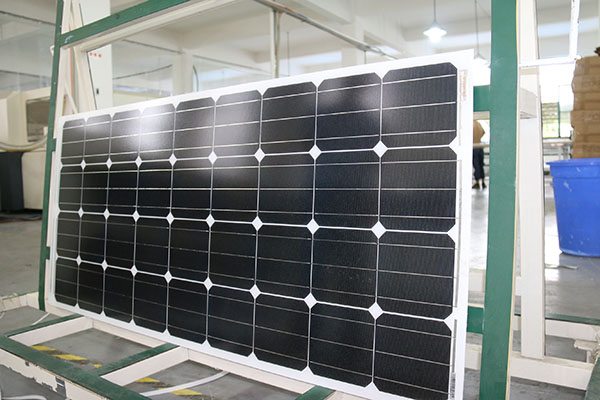
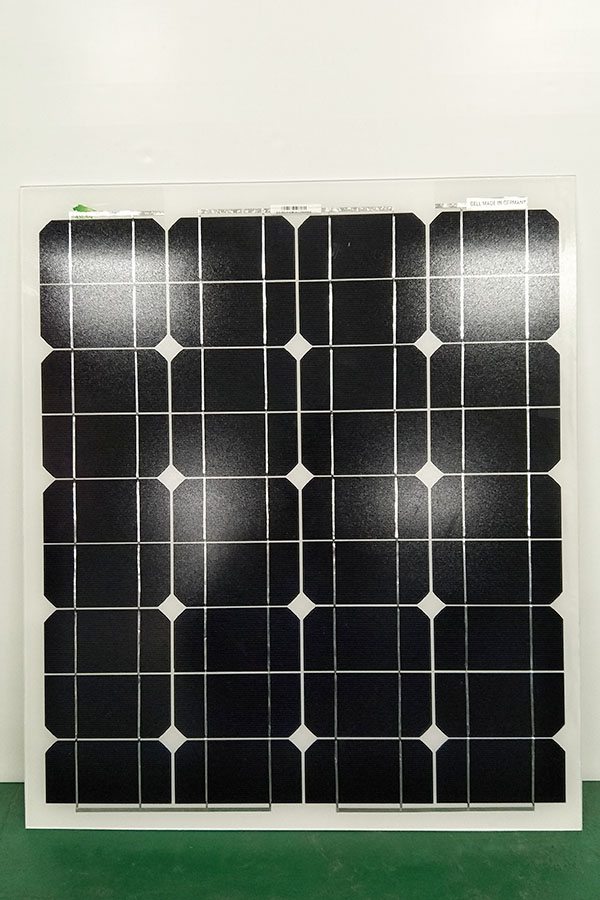
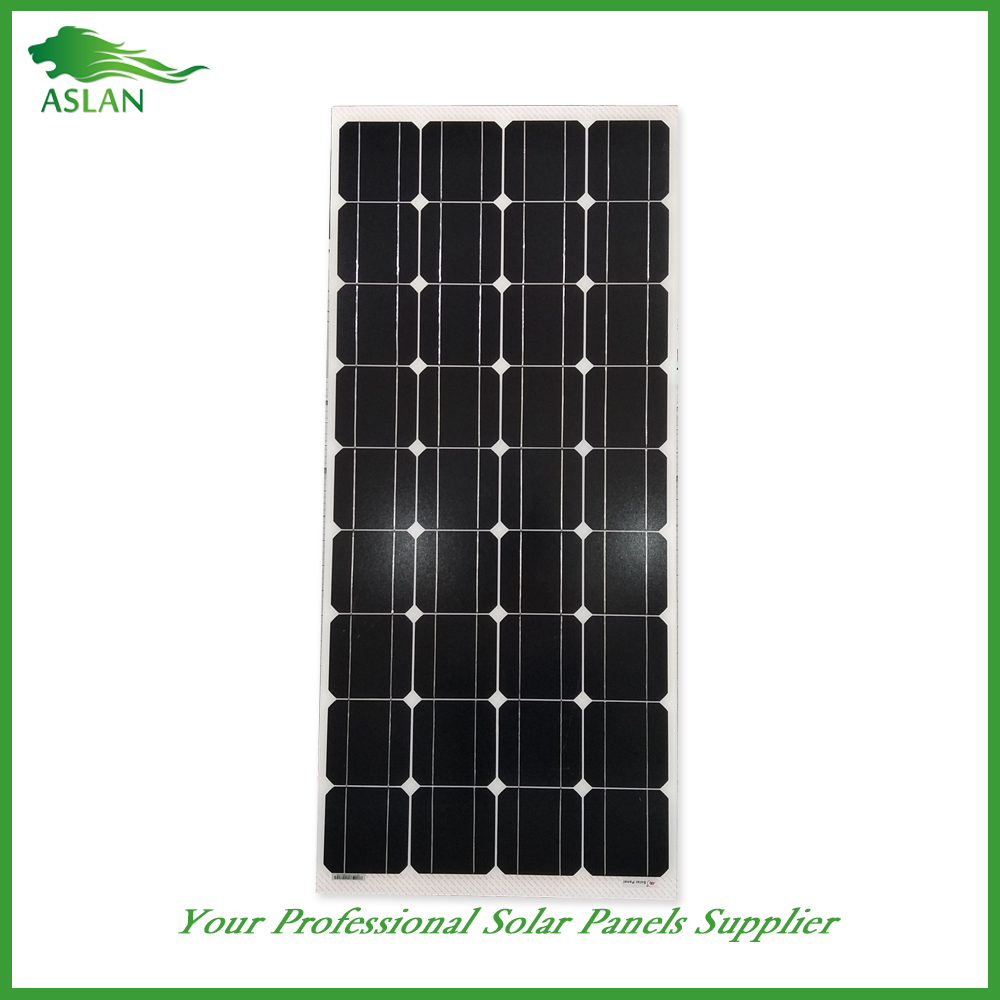
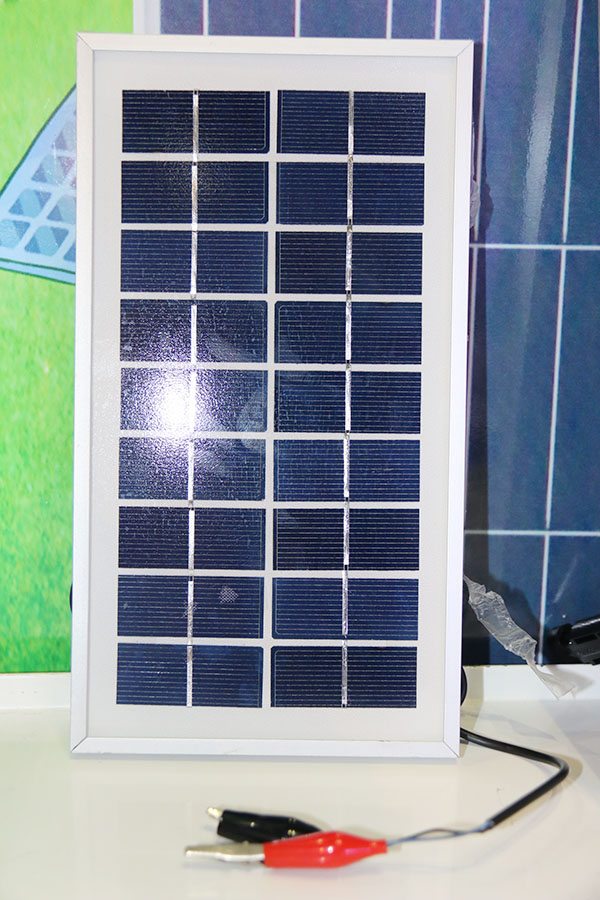
Mono-Crystalline 100W Solar Panel
Technical parameter
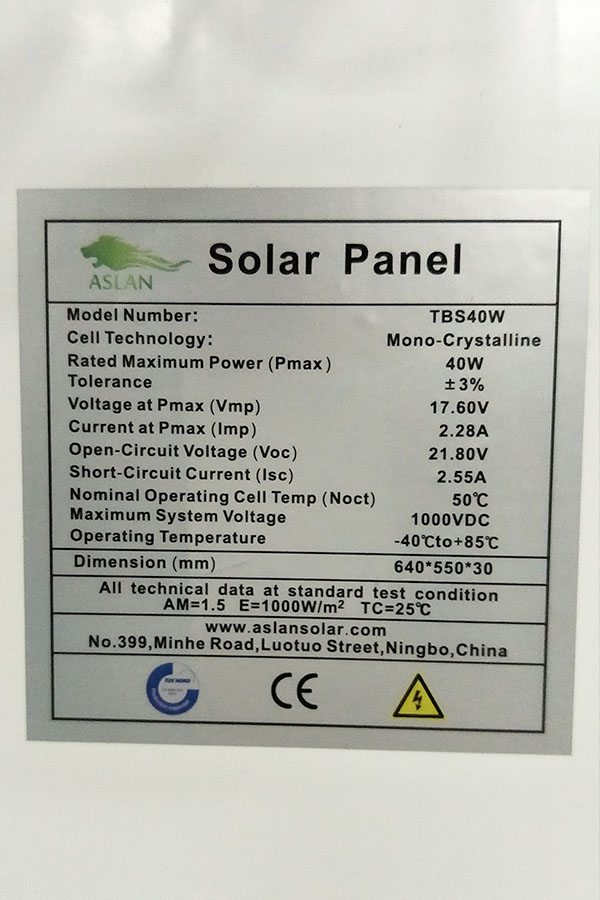
Maximum Power(W) 100W
Optimum Power Voltage(Vmp) 18.66V
Optimum Operating Current(Imp) 5.36A
Open Circuit Voltage(Voc) 22.72V
Short Circuit Current(Isc) 5.92A
Mechanical Characteristics
Cell Type Monocrystalline 125x125mm(5 inch)
No of Cell 36 (4x9pcs)
Dimensions 1200x554x35mm
Weight 7.8Kg
Front Glass 3.5mm,High Transmission, Low Iron,Tempered Glass
Junction box IP65 Rated
Output Cable TUV 1×4.0mm2/UL12AWG,Length:900mm
Temperature and Coefficients
Operating Temperature(°C): -40°C ~ + 85°C
Maximum System Voltage: 600V(UL)/1000V(IEC) DC
Maximum Rated Current Series: 15A
Temperature Coefficients of Pmax: -0.47%
Temperature Coefficients of Voc: -0.389%
Temperature Coefficients of Isc: 0.057%
Nominal Operationg Cell Temperature (NOCT): 47+/-2°C
Materials of solar panel
1).Solar Cell——Mono-crystalline solar cell 125*125mm
2).Front Glass——-3.2mm, high transmission, low iron, tempered glass
3).EVA——-excellent anti-aging EVA
4).TPT——-TPT hot seal made of flame resistance
5).Frame——anodized aluminum profile
6).Junction Box——-IP65 rated, high quality, with diode protection
Superiority: high quality anodized aluminum frame, high efficiency long life, easy installation, strong wind resistance, strong hail resistance.
Features
1. High cell efficiency with quality silicon materials for long term output stability
2. Strictly quality control ensure the stability and reliability, totally 23 QC procedures
3. High transmittance low iron tempered glass with enhanced stiffness and impact resistance
4. Both Polycrystalline and Mono-crystalline
5. Excellent performance in harsh weather
6. Outstanding electrical performance under high temperature and low irradiance
Quality assurance testing
Thermal cycling test
Thermal shock test
Thermal/Freezing and high humidity cycling test
Electrical isolation test
Hail impact test
Mechanical, wind and twist loading test
Salt mist test
Light and water-exposure test
Moist carbon dioxide/sulphur dioxide
✍️Quy trinh lắp đặt hệ thống pin năng lượng mặt trời chuyên nghiệp công ty VIMETCO
What is CRYSTALLINE SILICON? What does CRYSTALLINE SILICON mean? CRYSTALLINE SILICON meaning – CRYSTALLINE SILICON definition – CRYSTALLINE SILICON explanation.
Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ license.
Crystalline silicon (c-Si) is the crystalline forms of silicon, either multicrystalline silicon (multi-Si) consisting of small crystals, or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si), a continuous crystal. Crystalline silicon is the dominant semiconducting material used in photovoltaic technology for the production of solar cells. These cells are assembled into solar panels as part of a photovoltaic system to generate solar power from sunlight.
In electronics, crystalline silicon is typically the monocrystalline form of silicon, and is used for producing microchips. This silicon contains much lower impurity levels than those required for solar cells. Production of semiconductor grade silicon involves a chemical purification to produce hyperpure polysilicon followed by a recrystallization process to grow monocrystalline silicon. The cylindrical boules are then cut into wafers for further processing.
Solar cells made of crystalline silicon are often called conventional, traditional, or first generation solar cells, as they were developed in the 1950s and remained the most common type up to the present time. Because they are produced from 160–190 µm thick solar wafers—slices from bulks of solar grade silicon—they are sometimes called wafer-based solar cells.
Solar cells made from c-Si are single-junction cells and are generally more efficient than their rival technologies, which are the second-generation thin film solar cells, the most important being CdTe, CIGS, and amorphous silicon (a-Si). Amorphous silicon is an allotropic variant of silicon, and amorphous means “without shape” to describe its non-crystalline form.