Lowest Price for Poly-crystalline Solar Panel 60W for Germany
Short Description:
Our eternal pursuits are the attitude of "regard the market, regard the custom, regard the science" and the theory of "quality the basic, trust the first and management the advanced" for Lowest Price for Poly-crystalline Solar Panel 60W for Germany, We welcome new and old customers to contact us by phone or send us inquiries by mail for future business relationships and achieving mutual success.
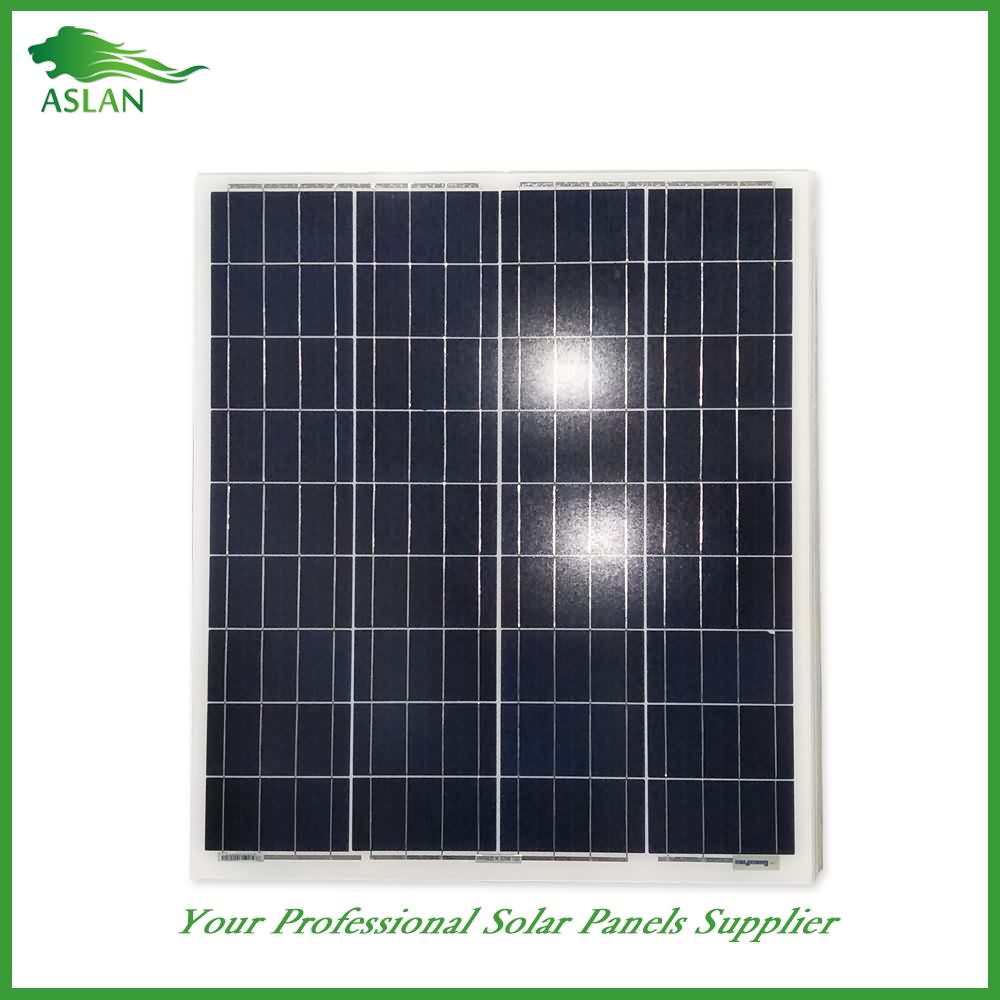
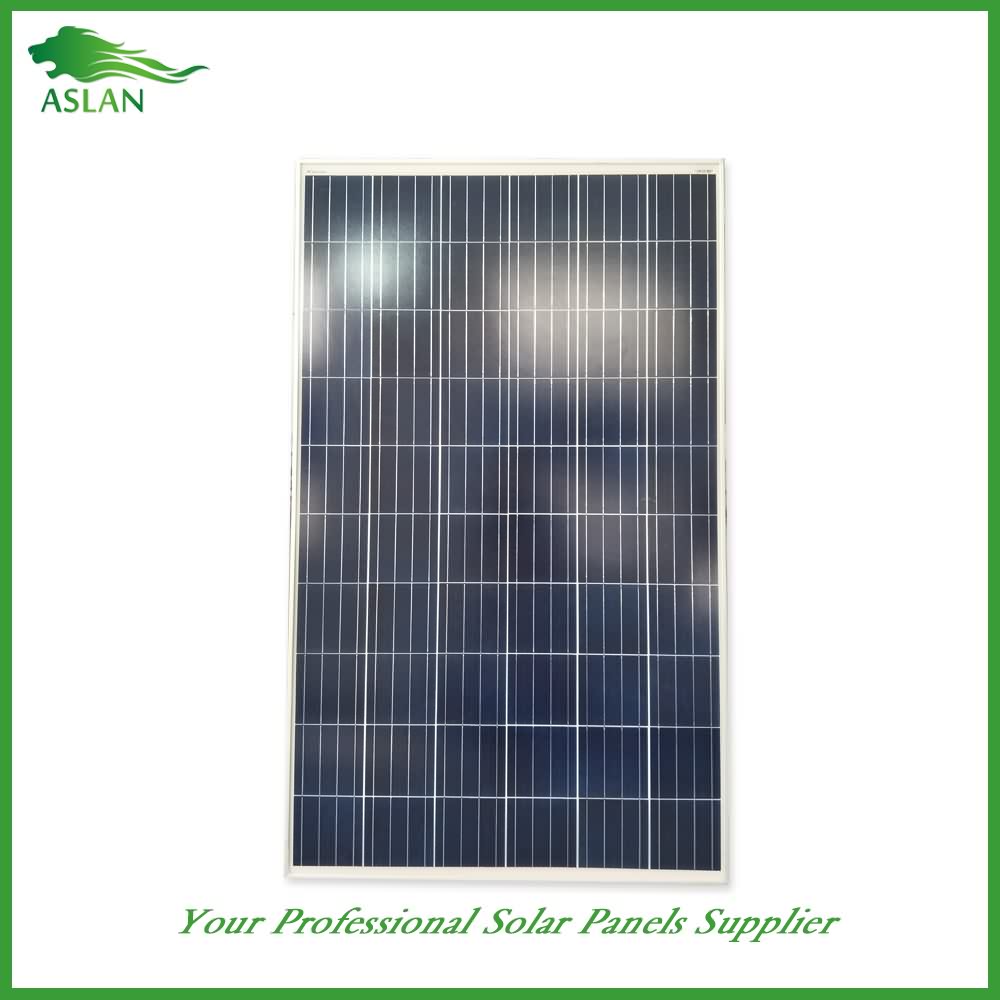
Poly-crystalline Solar Panel 60W
Technical parameter
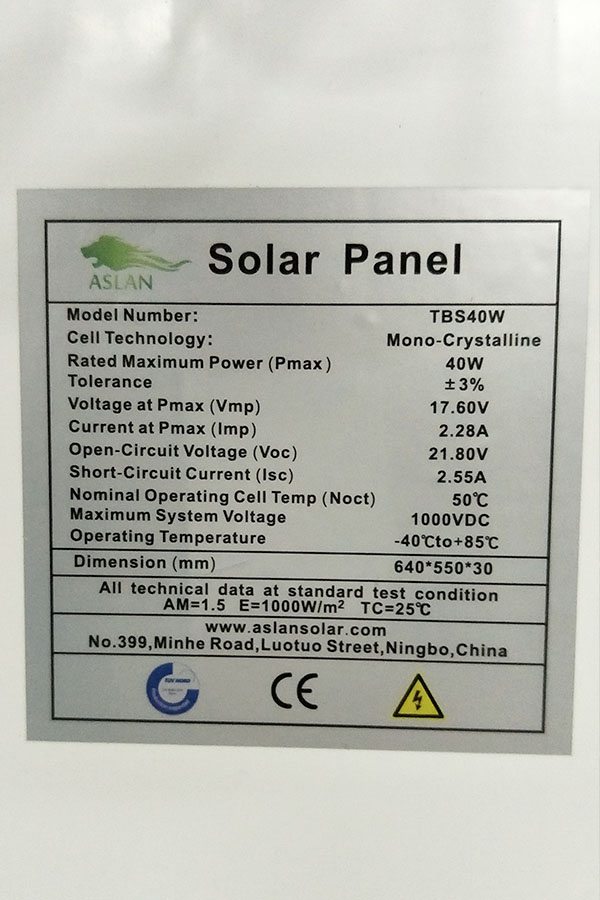
Maximum Power(W) 60W
Optimum Power Voltage(Vmp) 17.35V
Optimum Operating Current(Imp) 3.46A
Open Circuit Voltage(Voc) 21.16V
Short Circuit Current(Isc) 3.80A
Mechanical Characteristics
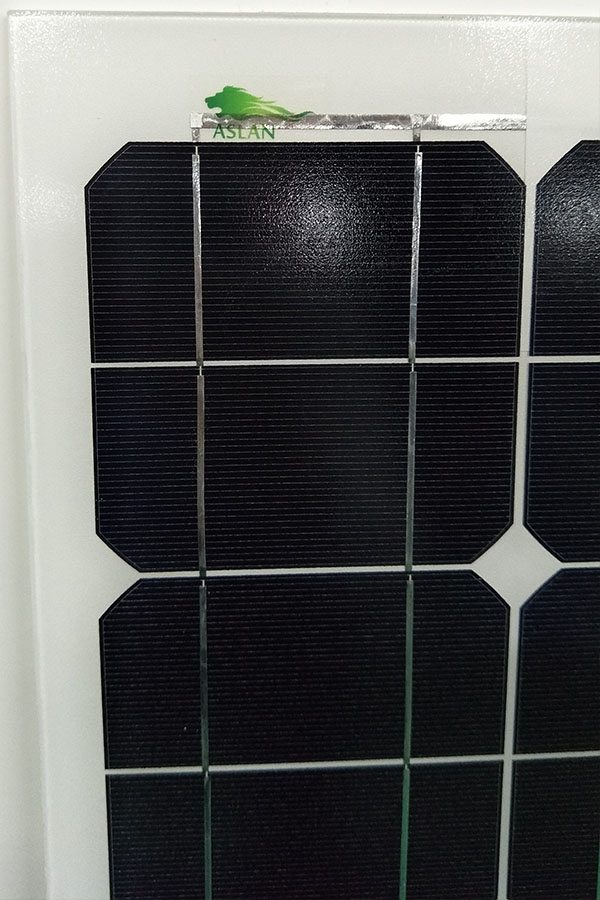
Cell Type Poly-crystalline 156 x 65mm
No of Cell 36 (4x9pcs)
Dimensions 678x657x35mm
Weight 5.0Kg
Front Glass 3.5mm,High Transmission, Low Iron,Tempered Glass
Junction box IP65 Rated
Output Cable TUV 1×4.0mm2/UL12AWG,Length:900mm
Temperature and Coefficients
Operating Temperature(°C): -40°C ~ + 85°C
Maximum System Voltage: 600V(UL)/1000V(IEC) DC
Maximum Rated Current Series: 15A
Temperature Coefficients of Pmax: -0.47%
Temperature Coefficients of Voc: -0.389%
Temperature Coefficients of Isc: 0.057%
Nominal Operationg Cell Temperature (NOCT): 47+/-2°C
Materials of solar panel
1).Solar Cell——Poly-crystalline solar cell 156*65mm
2).Front Glass——-3.2mm, high transmission, low iron, tempered glass
3).EVA——-excellent anti-aging EVA
4).TPT——-TPT hot seal made of flame resistance
5).Frame——anodized aluminum profile
6).Junction Box——-IP65 rated, high quality, with diode protection
Superiority: high quality anodized aluminum frame, high efficiency long life, easy installation, strong wind resistance, strong hail resistance.
Features
1. High cell efficiency with quality silicon materials for long term output stability
2. Strictly quality control ensure the stability and reliability, totally 23 QC procedures
3. High transmittance low iron tempered glass with enhanced stiffness and impact resistance
4. Both Poly-crystalline and Mono-crystalline
5. Excellent performance in harsh weather
6. Outstanding electrical performance under high temperature and low irradiance
Quality assurance testing
Thermal cycling test
Thermal shock test
Thermal/Freezing and high humidity cycling test
Electrical isolation test
Hail impact test
Mechanical, wind and twist loading test
Salt mist test
Light and water-exposure test
Moist carbon dioxide/sulphur dioxide
What is AMORPHOUS SILICON? What does AMORPHOUS SILICON mean? AMORPHOUS SILICON meaning – AMORPHOUS SILICON definition – AMORPHOUS SILICON explanation.
Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ license.
Amorphous silicon (a-Si) is the non-crystalline form of silicon used for solar cells and thin-film transistors in LCD displays.
Used as semiconductor material for a-Si solar cells, or thin-film silicon solar cells, it is deposited in thin films onto a variety of flexible substrates, such as glass, metal and plastic. Amorphous silicon cells generally feature low efficiency, but are one of the most environmentally friendly photovoltaic technologies, since they do not use any toxic heavy metals such as cadmium or lead.
As a second-generation thin-film solar cell technology, amorphous silicon was once expected to become a major contributor in the fast-growing worldwide photovoltaic market, but has since lost its significance due to strong competition from conventional crystalline silicon cells and other thin-film technologies such as CdTe and CIGS.
Amorphous silicon differs from other allotropic variations, such as monocrystalline silicon—a single crystal, and polycrystalline silicon, that consists of small grains, also known as crystallites.
Silicon is a fourfold coordinated atom that is normally tetrahedrally bonded to four neighboring silicon atoms. In crystalline silicon (c-Si) this tetrahedral structure continues over a large range, thus forming a well-ordered crystal lattice.
In amorphous silicon this long range order is not present. Rather, the atoms form a continuous random network. Moreover, not all the atoms within amorphous silicon are fourfold coordinated. Due to the disordered nature of the material some atoms have a dangling bond. Physically, these dangling bonds represent defects in the continuous random network and may cause anomalous electrical behavior.
The material can be passivated by hydrogen, which bonds to the dangling bonds and can reduce the dangling bond density by several orders of magnitude. Hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) has a sufficiently low amount of defects to be used within devices such as solar photovoltaic cells, particularly in the protocrystalline growth regime. However, hydrogenation is associated with light-induced degradation of the material, termed the Staebler–Wronski effect.
Amorphous alloys of silicon and carbon (amorphous silicon carbide, also hydrogenated, a-Si1-xCx:H) are an interesting variant. Introduction of carbon atoms adds extra degrees of freedom for control of the properties of the material. The film could also be made transparent to visible light.
Increasing concentrations of carbon in the alloy widen the electronic gap between conduction and valence bands (also called “optical gap” and bandgap). This can potentially increase the light efficiency of solar cells made with amorphous silicon carbide layers. On the other hand, the electronic properties as a semiconductor (mainly electron mobility), are adversely affected by the increasing content of carbon in the alloy, due to the increased disorder in the atomic network.
Several studies are found in the scientific literature, mainly investigating the effects of deposition parameters on electronic quality, but practical applications of amorphous silicon carbide in commercial devices are still lacking.
Unhydrogenated a-Si has a very high defect density which leads to undesirable semiconductor properties such as poor photoconductivity and prevents doping which is critical to engineering semiconductor properties. By introducing hydrogen during the fabrication of amorphous silicon, photoconductivity is significantly improved and doping is made possible. Hydrogenated amorphous silicon, a-Si:H, was first fabricated in 1969 by Chittick, Alexander and Sterling by deposition using a silane gas (SiH4) precursor. The resulting material showed a lower defect density and increased conductivity due to impurities. Interest in a-Si:H came when (in 1975), LeComber and Spear discovered the ability for substitutional doping of a-Si:H using phosphine (n-type) or diborane (p-type). The role of hydrogen in reducing defects was verified by Paul’s group at Harvard who found a hydrogen concentration of about 10 atomic % through IR vibration, which for Si-H bonds has a frequency of about 2000 cm-1. Starting in the 1970′s, a-Si:H was developed in solar cells by RCA by which steadily climbed in efficiency to about 13.6% in 2015.
How to Make Simple DC to AC Inverter. This video is demonstrates how easy it is to get this simple low power DC to AC. My first inverter circuit converts 8 – 30V DC to 120V AC and Over.
If you like my Demonstration-Experiment click the “like” Button. SUBSCRIBE► https://www.youtube.com/user/GIORGOSXANIOS?sub_confirmation=1 SHARE with your Friends… Feel free to post your Positive or Negative comment! SUPPORT my “work” DONATE for materials & equipments – Magnets & Magnet Wires, Lab TOOLS & any other building supplies, variable Power Supply ect. This would HELP my Research. Stay Tuned and Enjoy! https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_donations&business=GZEK5PYGW9D38&lc=GR&item_name=GEORGE%20CHANIOTAKIS God Bless Thanks-ELEMAN.
Cómo hacer simple DC a AC inversor. Este video se demuestra lo fácil que es conseguir este sencillo CC de baja potencia en AC. Mi primer circuito inversor convierte 8 – 30V DC a 120V AC y Over. Gracias por compartir. Disfrute …
Wie Einfache DC-AC Inverter Stellen. Dieses Video wird gezeigt, wie einfach es ist, diese einfache Low-Power-DC-AC zu erhalten. Meine erste Wechselrichterschaltung wandelt 8 – 30V DC bis 120 V AC und Over. Danke für das Teilen. Genießen Sie …
Comment faire simple DC à AC Inverter. Cette vidéo est démontre combien il est facile d’obtenir ce simple DC de faible puissance AC. Mon premier circuit inverseur convertit 8 – 30V DC à 120V AC et plus. Merci d’avoir partagé. Profitez …
Como fazer DC Simples de AC Inverter. Este vídeo é demonstrar como é fácil de obter este simples DC baixo poder de AC. Meu primeiro circuito inversor converte 8 – 30V DC para 120V AC e Over. Obrigado por compartilhar. Aproveite …
Come fare Simple CC a CA Inverter. Questo video dimostra come è facile ottenere questo semplice bassa CC a CA. Il mio primo circuito inverter converte 8 – 30V DC a 120V AC e Over. Grazie per la condivisione. Godetevi …
どのようにACインバーターへの単純なDCを作る。このビデオでは、それがACにこの単純な低電力DCを取得することがいかに簡単かを示しています。 120V ACおよびオーバーに30V DC – 私の最初のインバータ回路は8に変換します。共有をありがとう。お楽しみください…
Как сделать простой DC Инвертор переменного тока. Это видео демонстрирует, как легко это, чтобы получить эту простую низкую мощность постоянного тока в переменный. Моя первая схема Инвертор преобразует 8 – 30 В постоянного тока в 120 В переменного тока и выше. Спасибо, что поделился. Наслаждайтесь …
कैसे एसी इन्वर्टर करने के लिए सरल डीसी बनाने के लिए। इस वीडियो में यह एसी के लिए इस सरल कम बिजली डीसी पाने के लिए कितना आसान है यह दर्शाता है। 120V एसी और अधिक करने के लिए 30V डीसी – मेरी पहली पलटनेवाला सर्किट 8 धर्मान्तरित। साझा करने के लिए धन्यवाद। आनंद लें …
如何进行简单的直流到交流逆变器。这段视频演示了如何轻松地得到这个简单的低功耗直流到交流。我的第一个逆变器电路将8 – 30V DC到120V AC遍。感谢分享。享受…
Cum sa faci DC Simplu la AC invertor. Acest video este demonstrează cât de ușor este de a obtine acest simplu de alimentare CC redus la AC. Primul meu de circuit invertor convertește 8 – 30V DC la 120V curent alternativ și peste. Multumesc pentru partajarea. Bucurați-vă de …